Deferred revenues¶
Deferred revenues, or unearned revenues, are invoices addressed to customers for goods yet to be delivered or services yet to be rendered.
The company cannot report them on the current profit and loss statement, or income statement, since the goods and services will be effectively delivered/rendered in the future.
These future revenues must be deferred on the company’s balance sheet among the current liabilities until they can be recognized, at once or over a defined period, on the profit and loss statement.
For example, let’s say a business sells a software license of $1200 for 1 year. They immediately invoice it to the customer but can’t consider it earned yet, as the future months of licensing have not yet been delivered. Therefore, they post this new revenue in a deferred revenue account and recognize it on a monthly basis. Each month, for the next 12 months, $100 will be recognized as revenue.
Odoo Accounting handles deferred revenues by spreading them in multiple entries that are posted periodically.
Note
The server checks once a day if an entry must be posted. It might then take up to 24 hours before you see a change from Draft to Posted.
Configuration¶
Make sure the default settings are correctly configured for your business. To do so, go to . The following options are available:
- Journal
The deferral entries are posted in this journal.
- Deferred Revenue
Revenues are deferred on this Current Liability account until they are recognized.
- Generate Entries
By default, Odoo automatically generates the deferral entries when you post a customer invoice. However, you can also choose to generate them manually by selecting the Manually & Grouped option instead.
- Based on
There are three ways to calculate the deferred revenue recognition:
Days: The total amount is divided equally by the total number of days in the period, inclusive of the start and end dates.
Months: Each full month represents an equal proportion of the total amount, regardless of the actual number of days in that month (standardized basis).
Full Months: Any month started is treated as a complete month. However, the final month is only considered full if the period extends to the very last day of that month.
Suppose an invoice of $1200 must be deferred over 12 months.
The Days option accounts for different amounts depending on the number of days in each month (e.g., ~$102 for January and ~$92 for February).
The Months option accounts for $100 each month prorated to the number of days in that month (e.g., $50 for the first month if the Start Date is set to the 15th of the month).
The Full Months option considers each month started to be full (e.g., $100 for the first month even if the Start Date is set to the 15th of the month); this means that with the Full Months option, a full $100 is recognized in the first partial month, eliminating the need for a 13th month to recognize any remainder as would be the case when using the Months option.
Generate deferral entries on validation¶
Tip
Make sure the Deferred Date field is visible in the Invoice Lines tab. In most cases, the start of the deferred period should be in the same month as the Invoice Date. Deferred revenue entries are posted from the invoice date and are displayed in the report accordingly.
For each line of the invoice that should be deferred, specify the start and end dates of the deferral period.
If the Generate Entries field in the Settings is set to On invoice/bill validation, Odoo automatically generates the deferral entries when the invoice is validated. Click the Deferred Entries smart button to see them.
One entry, dated on the same day as the invoice’s accounting date, moves the invoice amounts from the income account to the deferred account. The other entries are deferral entries which, month after month, move the invoice amounts from the deferred account to the income account to recognize the revenue.
Example
You can defer a January invoice of $1200 over 12 months by specifying a start date of 01/01/2023 and an end date of 12/31/2023. At the end of August, $800 is recognized as an income, whereas $400 remains on the deferred account.
Reporting¶
The deferred revenue report computes an overview of the necessary deferral entries for each account. To access it, go to .
To view the journal items of each account, click on the account name and then Journal Items.
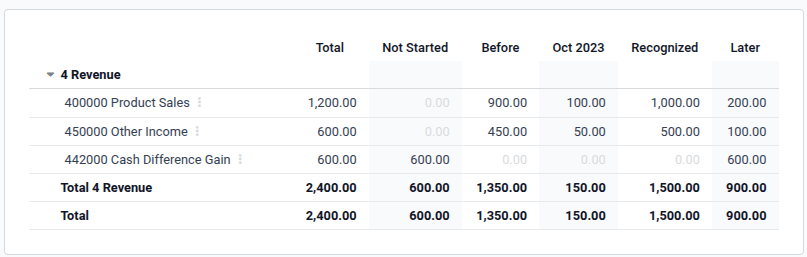
Note
Only invoices whose accounting date is before the end of the period of the report are taken into account.
Generate grouped deferral entries manually¶
If you have a lot of deferred revenues and wish to reduce the number of journal entries created, you can generate deferral entries manually. To do so, set the Generate Entries field in the Settings to Manually & Grouped. Odoo then aggregates the deferred amounts in a single entry.
At the end of each month, go to and click the Generate Entries button. This generates two deferral entries:
One dated at the end of the month which aggregates, for each account, all the deferred amounts of that month. This means that a part of the deferred revenue is recognized at the end of that period.
The reversal of this created entry, dated on the following day (i.e., the first day of the next month) to cancel the previous entry.
Example
There are three invoices deferred based on Months:
Invoice A: $1200 to be deferred from 01/01/2023 to 12/31/2023
Invoice B: $600 to be deferred from 01/01/2023 to 12/31/2023
Invoice C: $600 to be deferred in a future period (it will appear on the Not Started column)
- In January
At the end of January, after clicking the Generate Entries button, there are the following entries:
Entry 1 dated on the 31st January:
Line 1: Income account -1200 -600 -600 = -2400 (cancelling the total of all invoices)
Line 2: Income account 100 + 50 = 150 (recognizing 1/12 of invoice A and invoice B)
Line 3: Deferred account 2400 - 150 = 2250 (amount that has yet to be deferred later on)
Entry 2 dated on the 1st February, the reversal of the previous entry:
Line 1: Income account 2400
Line 3: Income account -150
Line 2: Deferred account -2250
- In February
At the end of February, after clicking the Generate Entries button, there are the following entries:
Entry 1 dated on the 28th February:
Line 1: Income account -1200 -600 -600 = -2400 (cancelling the total of all invoices)
Line 2: Income account 200 + 100 = 300 (recognizing 2/12 of invoice A and invoice B)
Line 3: Deferred account 2400 - 300 = 2100 (amount that has yet to be deferred later on)
Entry 2 dated on the 1st March, the reversal of the previous entry.
- From March to November
The same computation is done for each month until November.
- In December
There is no need to generate entries in December.
- In total
If we aggregate everything, we would have:
Invoice A and invoice B
Two entries (one for the deferral and one for the reversal) for each month from January to November
Invoice C will be deferred later
Therefore, at the end of December, invoices A and B are fully recognized as income only once in spite of all the created entries thanks to the reversal mechanism.